
Dairy foods offer a unique package of nutrients that work together to provide multiple health benefits for children and teens, including optimal growth and development, energy for active lifestyles and reduced risk of developing overweight and chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease later in life.
 Bone +
Muscle Development
Bone +
Muscle Development
 Dairy
is linked to improved bone health, especially in children and teens.1 Key nutrients like calcium, vitamin D and phosphorus in dairy help build strong bones and teeth and help prevent cavities.2
Dairy
is linked to improved bone health, especially in children and teens.1 Key nutrients like calcium, vitamin D and phosphorus in dairy help build strong bones and teeth and help prevent cavities.2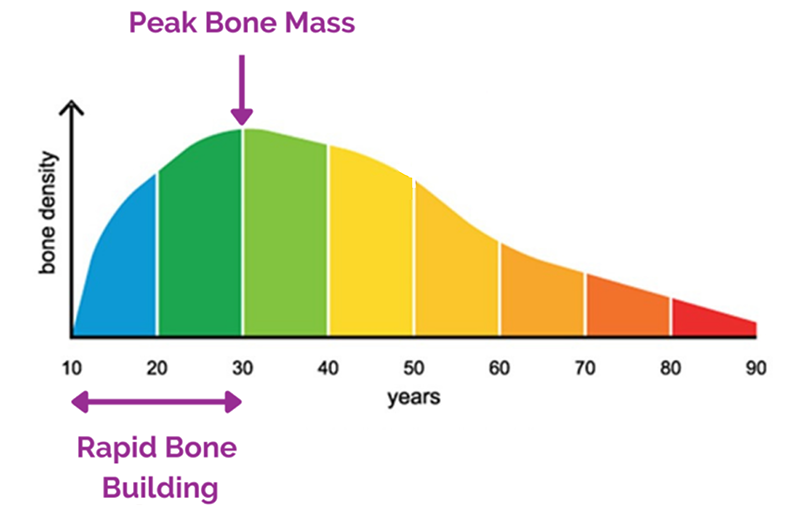
 Brain Development
Brain Development
 As part of a nutritious diet, dairy provides 7 of the 14 key nutrients required for brain development: iodine, choline, zinc, protein, and vitamins A, D and B12.4,5
As part of a nutritious diet, dairy provides 7 of the 14 key nutrients required for brain development: iodine, choline, zinc, protein, and vitamins A, D and B12.4,5


 Students
can enjoy milk and dairy foods at school through meal programs designed to meet specific nutrient needs and food requirements. Research shows that children who participate in these programs eat more nutrient dense and high-quality foods such
as milk, vegetables, fruits and whole grains than those who do not participate.13 Proper nutrition is associated with improved ability to focus and higher academic achievement.14
Students
can enjoy milk and dairy foods at school through meal programs designed to meet specific nutrient needs and food requirements. Research shows that children who participate in these programs eat more nutrient dense and high-quality foods such
as milk, vegetables, fruits and whole grains than those who do not participate.13 Proper nutrition is associated with improved ability to focus and higher academic achievement.14

 Lactose
Intolerant?
Lactose
Intolerant?
Pairing fruits, vegetables and whole grains with dairy for meals and snacks 3 times per day sets a foundation for lifelong healthy eating patterns.16
References
1. Heaney RP. Dairy and bone health. J Am Coll Nutr. 2009;28(Suppl1):82S-90S. DOI:10.1080/07315724.2009.10719808
2. Aili Li, et al. Research progress of milk and dairy products to prevent caries. Journal of Functional Foods. 2023;110:105837. DOI:10.1016/j.jff.2023.105837
3. Weaver CM, Gordon CM, Janz KF, et al. The National Osteoporosis Foundation’s position statement on peak bone mass development and lifestyle factors: a systematic review and implementation recommendations. Osteoporos Int .
2016;27:1281–1386.
DOI:10.1007/s00198-015-3440-3
4. Roberts M, Tolar-Peterson T, Reynolds A, Wall C, Reeder N, Rico Mendez G. The effects of nutritional interventions on the cognitive development of preschool-age children: A systematic review. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):532. DOI:10.3390/
nu14030532
5. Georgieff MK, Ramel SE, Cusick SE. Nutritional influences on brain development. Acta Paediatr. 2018;107(8):1310-1321. DOI:10.1111/apa.14287
6. Stress and health. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health website. October 1, 2021. Accessed November, 30 2023. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/stress-and-health
7. Desbrow B, Jansen S, Barrett A, Leveritt MD, Irwin C. Comparing the rehydration potential of different milk-based drinks to a carbohydrate–electrolyte beverage. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014;39(12):1366-1372. DOI:10.1139/apnm-2014-0174
8. Volterman KA, Obeid J, Wilk B, Timmons BW. Effect of milk consumption on rehydration in youth following exercise in the heat. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014;39(11):1257-1264. DOI:10.1139/apnm-2014-0047
9. Karp JR, Johnston JD, Tecklenburg S, Mickleborough TD, Flye AD, Stager JM. Chocolate milk as a post exercise recovery aid. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2006;16(1):78-91. DOI: 10.1123/ijsnem.16.1.78
10. National Dairy Council. 13 ways milk can help your body.2021. Accessed Nov 2022 at: https://www.usdairy.com/getmedia/0caf28ce-c6ce-4be0-adfd-dbc208f942a3/13-nutrients-in-milk-infographic-2021.pdf
11. Tardy A-L, Pouteau E, Marquez D, Yilmaz C, Scholey A. Vitamins and minerals for energy, fatigue and cognition: A narrative review of the biochemical and clinical evidence. Nutrients.2020;12(1):228. DOI:10.3390/nu12010228
12. Calder PC. Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections. Nutrients. 2020;12(4). DOI: 10.3390/nu12041181
13. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. School Meals. Updated October, 19 2022. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/nutrition/schoolmeals.htm
14. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Health and Academic Achievement.
Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/nutrition/schoolmeals.htm
15. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. School nutrition and the social and emotional climate and learning. September 21, 2021. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/nutrition/school_nutrition_sec.htm#:~:text=Providing%20nutrition%20education%20can%20teach,of%20feeling%20hungry%20and%20full.&text=Encouraging%20teachers%20to%20eat%20meals,and%20strengthen%20relationships%20with%20students
16. US Department of Agriculture and US Department of Health and Human
Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. 9th ed. 2020.
Accessed November, 30 2023. https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/resources/2020-2025-dietary-guidelines-online-materials

Older adults have unique nutritional needs that support optimal health and enhance quality of life during aging.

Nutrition during pregnancy and early childhood lays the foundation for optimal health, cognitive abilities, motor skills and more.